Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative technology that has been shaping various sectors of our society. At its core, AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
Early Developments
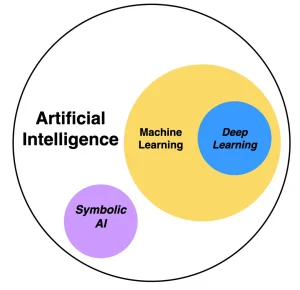
The concept of artificial intelligence is not new. It dates back to the mid-20th century when the first AI programs were developed. The term “Artificial Intelligence” was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 during the Dartmouth Conference, which is considered the birthplace of AI as an academic discipline. Early AI research focused on problem-solving and symbolic methods.
The Rise of Machine Learning
In the 1980s, the field saw a significant shift with the advent of machine learning, a subset of AI. Unlike traditional AI, where rules are explicitly programmed, machine learning enables systems to learn from data. This paradigm shift was facilitated by the development of algorithms that could automatically improve through experience.
Deep Learning and Modern AI
The 21st century brought about deep learning, a subset of machine learning characterized by neural networks with many layers. Deep learning has been the driving force behind many of the most significant AI advancements, including speech recognition, image recognition, and natural language processing.
Types of AI
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed and trained for a specific task. Virtual personal assistants like Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa are examples of narrow AI. They perform limited tasks, such as setting reminders, searching for information online, and controlling smart home devices.
General AI
General AI, or Strong AI, refers to systems that possess the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can do. This level of AI is still theoretical and does not exist yet. General AI would have the capacity to understand, learn, and apply knowledge in different contexts, making it indistinguishable from human intelligence.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI surpasses human intelligence and capabilities. It is an AI that can perform tasks better than the best human minds in every field, including scientific creativity, general wisdom, and social skills. While this concept is still speculative, it raises important ethical and existential questions about the future of humanity.
Applications of AI
Healthcare
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and advanced medical research. Machine learning algorithms can analyze medical images, predict disease outbreaks, and even assist in robotic surgeries.
Finance
In the finance industry, AI is used for algorithmic trading, fraud detection, credit scoring, and personalized financial advice. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time, providing insights that were previously impossible to obtain.
Transportation
AI is at the heart of autonomous vehicles, which promise to reduce accidents and improve traffic flow. AI systems in transportation can optimize routes, predict maintenance needs, and enhance the overall efficiency of logistics and supply chain management.
Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service by providing instant responses and personalized interactions. These systems can handle a wide range of queries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Education
AI is enhancing education through personalized learning experiences, automated grading, and intelligent tutoring systems. AI-driven platforms can adapt to the learning pace and style of individual students, making education more accessible and effective.
Ethical Considerations in AI
Bias and Fairness
AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased, the AI’s decisions will be biased as well. Ensuring fairness and avoiding discrimination in AI algorithms is a critical challenge that researchers and developers must address.
Privacy and Security
The use of AI in data analysis raises significant privacy concerns. It is essential to establish robust data protection measures to safeguard personal information. Additionally, AI systems must be designed to be secure against cyberattacks and misuse.
Job Displacement
While AI has the potential to create new job opportunities, it also poses the risk of job displacement. Automation of routine tasks could lead to unemployment in certain sectors. It is crucial to implement policies that support workforce transition and retraining.
Accountability and Transparency
As AI systems become more complex, understanding their decision-making processes becomes challenging. Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI operations is vital to build trust and avoid unintended consequences.
YOU MAY ALSO READ: Does a WordPress Developer Need Coding Skills?
The Future of AI
AI and Human Collaboration
The future of AI lies in the collaboration between humans and machines. AI can augment human capabilities, allowing us to solve complex problems and achieve unprecedented levels of innovation. Emphasizing a collaborative approach will enable us to harness the full potential of AI while mitigating its risks.
Continued Advancements
Research in AI is advancing at a rapid pace. Emerging technologies like quantum computing, neuromorphic engineering, and advanced robotics hold the promise of further revolutionizing AI. These advancements will likely lead to new applications and improvements in existing AI systems.
Regulatory Frameworks
To ensure the responsible development and deployment of AI, robust regulatory frameworks are necessary. These frameworks should address ethical concerns, promote transparency, and foster innovation while protecting public interest.
Conclusion.
Artificial Intelligence is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field that holds immense potential to transform various aspects of our lives. From healthcare to finance, education to transportation, AI is making significant strides in improving efficiency, accuracy, and personalization. However, it also brings forth ethical and societal challenges that must be carefully navigated. By fostering collaboration, advancing research, and implementing effective regulations, we can ensure that AI serves as a powerful tool for the betterment of humanity.



